CBD vs THC: Effects, Uses and Legal Differences

CBD and THC may come from the same plant, but they couldn't be more different. Here's what every beginner should know about how they work, how they feel, and why it matters.
From potentially easing stress to promoting sleep, CBD is a popular wellness supplement, but it's just one of many compounds in the cannabis plant. Unlike THC, which causes a “high”, CBD works differently and is non-intoxicating.
In this beginner-friendly guide, we'll explore the difference between CBD and THC, how other cannabinoids like CBG, CBN and CBC compare, and what you need to know about these lesser-known cannabinoids.
What are cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found in the cannabis plant. Scientists have identified over 100 different cannabinoids, each with its own potential effects on the body and mind. The most well-known are CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), but there are minor cannabinoids like CBG, CBN and CBC that are gaining attention for their unique properties.
These compounds interact with a complex network in the body known as the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which helps regulate key functions, including mood, sleep, appetite, immune response, and pain. Rather than directly causing specific effects, cannabinoids are thought to support the ECS in maintaining balance, or what scientists call homeostasis.
Cannabinoids are often grouped into two categories:
- Major cannabinoids: These include CBD and THC, which are typically found in higher concentrations and are the most extensively researched.
- Minor cannabinoids: These include CBG (cannabigerol), CBN (cannabinol), and CBC (cannabichromene). Although present in smaller amounts, early studies suggest they may have valuable wellness applications of their own.
As interest in natural health grows, so does curiosity about how these different cannabinoids compare and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Where can cannabinoids be found?
As mentioned, cannabinoids like CBD, THC and others are found naturally in cannabis, including both hemp and marijuana varieties. These compounds are primarily concentrated in the plant's flowers and resin.
But not all cannabis is the same. In fact, “What's the difference between CBD, THC, marijuana and hemp?” is one of the most common questions among new users. Here's a handy breakdown:
- Hemp is a type of cannabis bred to be high in CBD and naturally low in THC (below 0.2%). It's the legal source of most CBD products available in Europe.
- Marijuana, on the other hand, typically contains higher levels of THC, the psychoactive compound responsible for producing a “high”. Marijuana remains illegal in much of the modern world.
- CBD is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid extracted mostly from hemp. It's used in oils, capsules, edibles and skincare products for potential wellness support.
- THC is found in both hemp and marijuana, but only in trace amounts in hemp. Its mind-altering effects are the main reason marijuana is tightly regulated.
So while CBD and THC come from the same plant species, their legal status, effects and sources differ significantly. Understanding these distinctions can help you make informed choices when exploring cannabinoid-based products.
What is CBD?
CBD, or cannabidiol, is one of the most well-known cannabinoids found in hemp. Unlike THC, it's non-psychoactive, meaning it won't make you feel high. Instead, it interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system (ECS), a network that helps regulate mood, sleep, pain and overall balance.
People commonly use CBD to support stress relief, better sleep, pain management and skin health. While research is still in development, many users report noticeable benefits with consistent use, especially when CBD is part of a comprehensive wellness routine.
In many European countries, CBD is legal if it's derived from approved hemp strains that contain less than 0.2% THC. It's widely available in oils, capsules, creams and more, provided the products meet safety and labelling standards.
What is THC?

THC, short for tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, responsible for the “high” or altered state often linked with marijuana use. It binds directly to the receptors in the brain's endocannabinoid system, influencing mood, memory and perception.
While best known for its recreational use, THC also has medical applications. It may help alleviate pain, nausea, stimulate appetite, and manage certain neurological conditions. In some countries, it's available by prescription as part of cannabis-based medicines.
In many countries, however, THC is a controlled substance. It's illegal to buy or possess products containing THC without a prescription, and over-the-counter supplements must contain only trace amounts to be legally sold.
CBD vs THC: Key differences
When it comes to CBD vs THC, the two cannabinoids may come from the same plant, but they work very differently in the body. While both interact with the endocannabinoid system, only THC produces psychoactive effects.
So, is CBD better than THC for you? That depends on your goals, sensitivity to THC, and whether you're seeking therapeutic effects with or without intoxication. Below is a simple breakdown of the key differences to help you decide:
Psychoactivity:
- CBD is non-psychoactive: it won't make you feel high.
- THC is psychoactive and produces a noticeable high.
Legal status:
- CBD is legal if it comes from approved hemp that contains less than 0.2% THC.
- THC is a controlled substance and is only legal with a medical prescription in some countries.
Medical uses:
- CBD may support stress relief, sleep, pain management and skin health.
- THC is used medically for pain, nausea, appetite stimulation and conditions like MS.
Availability:
- CBD is widely available in oils, capsules, creams, edibles and more.
- THC is only available in the UK and a handful of other European countries via prescription through specific cannabis-based medicines.
Safety:
- CBD is generally well-tolerated with minimal side effects.
- THC can cause drowsiness, anxiety, dry mouth or impaired coordination in some users.
While both compounds may offer therapeutic value, CBD is often preferred by wellness-focused users looking for balance without intoxication or legal complications. THC, on the other hand, may be more suitable in clinical settings under medical supervision.
Does CBD get you high like THC does?
No, CBD does not get you high. Unlike THC, which is psychoactive and alters perception, CBD is non-intoxicating. That means it won't cause euphoria, impairment or the typical “high” associated with cannabis use.
Instead of directly activating the brain's cannabinoid receptors as THC does, CBD works more indirectly. It's believed to help support balance in the body by interacting with the endocannabinoid system, which regulates functions such as mood, sleep, and pain.
Many people choose CBD specifically because it offers potential wellness benefits without any mind-altering effects. That's also one of the main reasons it's legal and widely available in the UK, while THC remains strictly regulated.
What about other cannabinoids?
While CBD and THC are the most well-known cannabinoids, they're only part of the picture. The cannabis plant produces over 100 different cannabinoids, many of which are still being studied for their unique effects and potential wellness benefits.
These minor cannabinoids typically do not appear in large amounts, but early research suggests they may play crucial roles in supporting overall health. They often work alongside CBD and THC in what's known as the “entourage effect”, a theory that cannabinoids may have stronger or more balanced effects when used together.
Here are three of the most researched minor cannabinoids so far, and how they differ from CBD.
CBG
CBG (cannabigerol) is often referred to as the “mother cannabinoid” because it's the precursor from which other cannabinoids, including CBD and THC, are formed. While usually found in small amounts, it has become increasingly popular due to its potential anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and neuroprotective effects.
Early studies suggest that CBG may support focus, gut health, and mood balance; however, further research is needed.1 Like CBD, CBG is non-psychoactive, meaning it won't produce a high.
CBN
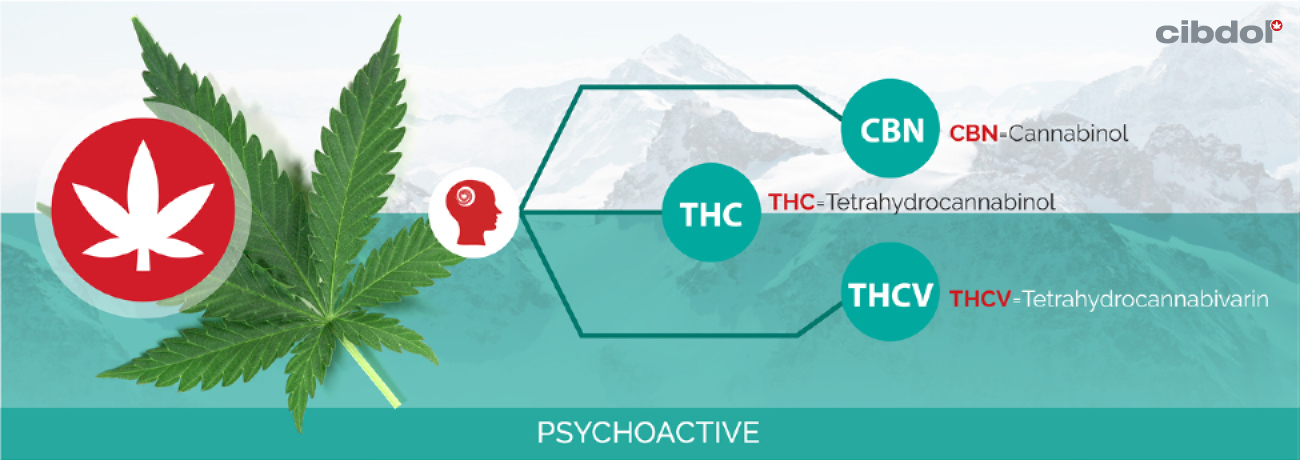
CBN (cannabinol) is a mildly psychoactive cannabinoid that forms as THC ages and breaks down. It's most commonly associated with sleep support and is often included in nighttime CBD blends.
Some early research suggests CBN may have some sedative properties, although its effects are still not fully understood.2 It may also play a role in pain relief and inflammation, but like other minor cannabinoids, its benefits remain under investigation.
CBC
CBC (cannabichromene) is another non-psychoactive cannabinoid that may contribute to the entourage effect. It has shown potential in early studies for mood regulation, pain relief and skin health, particularly through its interaction with receptors related to inflammation and serotonin.3
Though less well-known than CBD or THC, CBC may become more widely used as research into its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects continues to grow.
Choosing the right cannabinoid for you
With numerous cannabinoids to explore, it's essential to find the one that best aligns with your personal wellness goals. Whether you're looking to unwind, sleep better, ease physical discomfort, or stay focused, different compounds may offer various types of support.
Although these cannabinoids may interact with users differently, some individuals will find that certain cannabinoids work more effectively than others. In contrast, others might not experience any benefits; they should not be treated as a miracle cure or quick fix.
For anxiety and stress relief
Many people turn to CBD or CBG for potential soothing effects without intoxication. These non-psychoactive cannabinoids may help regulate mood by interacting with serotonin and ECS pathways.
For sleep support
Many nighttime formulas include CBN for its possible sedative properties. CBD may also promote better sleep by reducing stress and supporting the body's natural rhythms.
For pain or recovery
Both CBD and CBC are being explored for their potential anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. THC may also be effective in medical settings.
For focus and clarity
CBG is gaining attention for its potential cognitive and energy-boosting effects, particularly in daytime formulations that minimise sedation.
Product types to consider
Once you've identified your goal, the next step is choosing a CBD product format that suits your lifestyle and preferences:
- Oils and tinctures: Fast absorption, flexible dosing and ideal for everyday balance.
- Capsules and softgels: Convenient and tasteless, great for consistent daily use.
- Edibles (gummies, etc): Slow-release and enjoyable, but less precise for dosing.
- Topicals: Applied to the skin for localised relief from soreness or irritation.
- Vapes: Fast-acting but not suitable for everyone; use with caution, especially if new to cannabinoids.
Navigating the world of cannabinoids
From CBD and THC to emerging compounds like CBG, CBN and CBC, cannabinoids offer a growing range of natural options to support your well-being. While they all come from the same plant, each cannabinoid has unique properties, from CBD's non-psychoactive soothing effects to THC's stronger, prescription-only applications.
Understanding the difference between CBD and THC, along with how minor cannabinoids compare to CBD, can help you choose the right fit for your goals, whether it's stress relief, improved sleep, pain support, or enhanced focus.
For most wellness users, CBD remains the most accessible and widely used cannabinoid, offering potential benefits without the high or legal restrictions. However, as research evolves, other cannabinoids are gaining popularity in targeted blends and products.
Whether you're new to cannabinoids or refining your wellness routine, taking the time to understand each compound can help you make more informed, effective choices. As interest in natural health grows, so does the importance of choosing high-quality, lab-tested products you can trust. Start with low doses, listen to your body, and speak with a healthcare professional if you have any questions. Remember, the right cannabinoid for you is the one that best supports your personal path to balance and well-being.
References
- Anokwuru CP, Makolo FL, Maxleene Sandasi, et al. Cannabigerol: a bibliometric overview and review of research on an important phytocannabinoid. Phytochemistry Reviews. 2022;21(5):1523-1547. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-021-09794-w ↩︎
- Bonn-Miller MO, Feldner MT, Bynion TM, et al. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of the safety and effects of CBN with and without CBD on sleep quality. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2023;32(3). doi:https://doi.org/10.1037/pha0000682 ↩︎
- Sepulveda DE, Vrana KE, Kellogg JJ, et al. The Potential of Cannabichromene (CBC) as a Therapeutic Agent. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. Published online May 22, 2024:JPET-MR-2024-002166. doi:https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.124.002166 ↩︎