The Role of Collagen for Skin Health Explained
Published:
Categories: CollagenWhat is Collagen and Why is it Important for Skin Health?
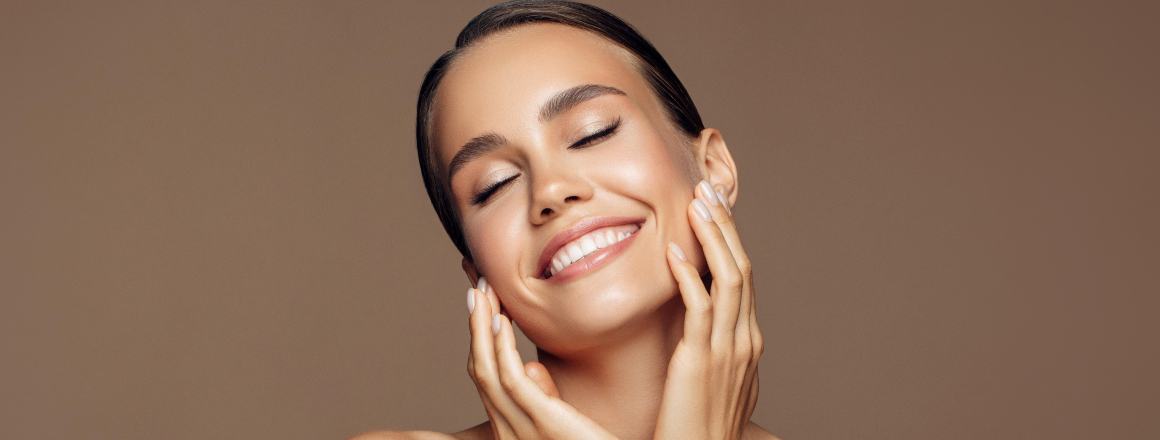
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, making up 75-80% of our skin. It provides structure and strength to our skin, helping to maintain elasticity and prevent sagging. As we age, our bodies produce less and less collagen, leading to wrinkles, fine lines, and thinner skin. Taking collagen supplements or using collagen-boosting skincare can help counteract this natural decline.
Contents:

The Structure and Function of Collagen in Skin
Collagen has a unique rope-like helical structure that allows many collagen fibers to crosslink and form sheets or networks. This provides structural support to connective tissue like skin dermis, bones, tendons, and ligaments. In our skin, networks of collagen keep the epidermis attached to the dermis layer underneath.
The most abundant types of collagen in skin are:
- Type I collagen - Forms fibers and gives tensile strength. Found throughout the body and in scar tissue.
- Type III collagen - Forms reticular networks. Supports structure of expansive organs like skin dermis.
- Type IV collagen - Forms basement membrane sheets. Attaches epidermis to dermis.
- Type XVII collagen - Anchors between dermis and epidermis at hemidesmosomes.
As we age, collagen networks deteriorate and individual fibers become increasingly disorganized. The skin gets thinner, less dense, drier, and loses elasticity. Exposure to UV rays from the sun also damages and breaks down collagen.
How Collagen Helps Reduce Signs of Aging
By middle age, our body may produce only half as much collagen as it did in our youth. This collagen loss leads to common aging signs like:
- Fine lines and wrinkles
- Loss of elasticity and sagging skin
- Thin, fragile, easily damaged skin
- Loss of facial volume/hollowness in cheeks
- Dullness, dryness, flakiness
Clinical studies show oral collagen supplementation can increase skin hydration, elasticity, and dermal collagen density. Daily collagen helps combat natural collagen decline, supporting thinner skin, reducing wrinkles, and keeping skin supple.
Collagen peptides are absorbed by the intestines and travel through the bloodstream to various tissues like skin that need repair. New collagen fibers produced with the help of collagen peptides reinforce the dermal matrix and stimulate skin cells like fibroblasts and keratinocytes.
Skin also appears plumper with the extra hydration and volume provided by collagen fragments. Many people notice their face looks fuller and more youthful after taking a collagen supplement for just 4-8 weeks.
Top 6 Science-Backed Collagen Benefits for Skin
Here are some of the top ways research shows collagen can improve skin health and combat signs of aging:
1. Increases Skin Hydration and Moisture
Collagen peptides increase synthesis of hyaluronic acid, a powerful humectant that attracts and binds moisture within the dermis. This helps maintain skin hydration, plumpness and overall appearance.
In one study, oral collagen caused significant improvement in facial skin moisture after 8 weeks of use in women aged 35-55. Skin hydration increased by 28% on average.
2. Reduces Facial Wrinkles and Fine Lines
By stimulating new collagen, peptides can help fill in wrinkles and fine lines from the inside out. Several studies show a reduction in depth of wrinkles after taking collagen supplements for 2-3 months.
In a double-blind trial, women taking collagen hydrolysate for 8 weeks experienced a significant reduction in eye wrinkle volume compared to placebo.
3. Improves Elasticity and Tightens Sagging Skin
Collagen peptides boost production of elastin proteins that maintain skin's springiness and resistance to stretching. Enhancing dermal elastin content improves texture, elasticity, and firmness of facial skin.
In clinical studies, oral collagen resulted in considerable improvements in skin elasticity over 3-6 months of use. One study showed a 9% average increase in skin elasticity.
4. Protects Against UV Damage and Photoaging
Some evidence indicates oral collagen may protect dermal collagen fibers and skin cells from degradation caused by UV radiation. It may also help repair sun-damaged skin faster.
Several studies note benefits for reducing visible signs of photoaging. One found collagen peptides decreased UV-induced redness and pigmentation. Another saw increased skin moisture and elasticity while reducing wrinkles in women with sun-damaged skin.
5. Regulates Collagen Synthesis in Aging Skin
Our skin loses the ability to properly synthesize and rebuild collagen as we get older. Collagen supplements provide a direct supply of peptide building blocks that can stimulate collagen production and slow its deterioration in aging skin.
Multiple human trials show collagen peptide intake increases collagen content, densities, and thickness of skin over time. One double-blind study found it boosted collagen density in the dermis by 6% after just 4 weeks.
6. Improves Overall Appearance of Aging Skin
In studies assessing cosmetic effects of collagen supplements, researchers consistently observe significant improvements in overall skin condition - including facial contours, fine lines, wrinkles, moisture levels, radiance, smoothness, and firmness.
One clinical trial found 69% of women reported improvements in overall facial skin appearance after taking collagen daily for only 1 month.
Best Collagen Sources for Your Skin
The body can produce collagen from amino acids in protein-rich foods. However, cooking denatures the protein structure, making it more difficult to metabolize and use for collagen synthesis.
Consuming enzymatically hydrolyzed collagen supplements provides collagen in its optimal bioavailable form. Collagen peptides are highly absorbable - up to 90-95% - thanks to the hydrolysis process that breaks collagen into small fragments.
Here are excellent collagen sources to fight skin aging:
- Marine Collagen - Made from fish skin and scales. More absorbable than mammalian collagen with smaller peptides. Helps build type I collagen.
- Bovine Collagen - Made from cow hides. Closely matches human collagen structure. Very cost effective source.
- Eggshell Membrane Collagen - Made from eggshell membranes. Concentrated source of highly bioavailable collagen peptides.
- Multi-Source Collagen - Combines bovine, marine, and eggshell collagen peptides. Provides balanced amino acid profile for comprehensive anti-aging effects.
Look for a natural, high-purity hydrolyzed collagen containing at least 10-15 grams protein per serving. Powder collagen dissolves easily in water or smoothies for convenience.
Aim for daily collagen intake of 5-15 grams. Most people see benefits consuming 10 grams daily. Effects appear after 4 weeks and improve with consistent long-term use of 2-3 months.
The Role of Collagen for Skin Health Explained. Conclusion
Collagen plays a vital structural role in our skin. Age-related collagen decline leads to wrinkles, sagging, and loss of elasticity. Supplementing with bioavailable hydrolyzed collagen peptides can stimulate collagen synthesis and combat signs of skin aging.
Research shows consistent use of a quality collagen supplement promotes hydration, elasticity, firmness and overall younger-looking skin by replenishing the dermal collagen matrix. Collagen works from the inside out to reduce wrinkles, tighten skin, and restore a more youthful complexion.
Resources used to write this article
Asserin, J., Lati, E., Shioya, T., & Prawitt, J. (2015). The effect of oral collagen peptide supplementation on skin moisture and the dermal collagen network: evidence from an ex vivo model and randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 14(4), 291–301. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12174
Proksch, E., Schunck, M., Zague, V., Segger, D., Degwert, J., & Oesser, S. (2014). Oral intake of specific bioactive collagen peptides reduces skin wrinkles and increases dermal matrix synthesis. Skin pharmacology and physiology, 27(3), 113–119. https://doi.org/10.1159/000355523
Choi, S. Y., Ko, E. J., Lee, Y. H., Kim, B. G., Shin, H. J., Seo, D. B., Lee, S. J., Kim, B. J., & Kim, M. N. (2020). Effects of collagen tripeptide supplement on skin properties: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. Journal of cosmetic dermatology, 19(3), 732–737. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13127
Schwartz, S. R., & Park, J. (2012). Ingestion of BioCell Collagen®, a novel hydrolyzed chicken sternal cartilage extract; enhanced blood microcirculation and reduced facial aging signs. Clinical interventions in aging, 7, 267–273. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S32836
Inoue, N., Sugihara, F., Wang, X. (2016). Ingestion of bioactive collagen hydrolysates enhance facial skin moisture and elasticity and reduce facial ageing signs in a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled clinical study. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 96(12), 4077-4081. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7606
Tanaka, M., Koyama, Y., Nomura, Y. (2009). Effects of Collagen Peptide Ingestion on UV-B-Induced Skin Damage. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 73(4), 930-932. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.80649
Sign up to our newsletter and enjoy 10% off one order
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE
Post related products
-

Look Younger CIBD0073