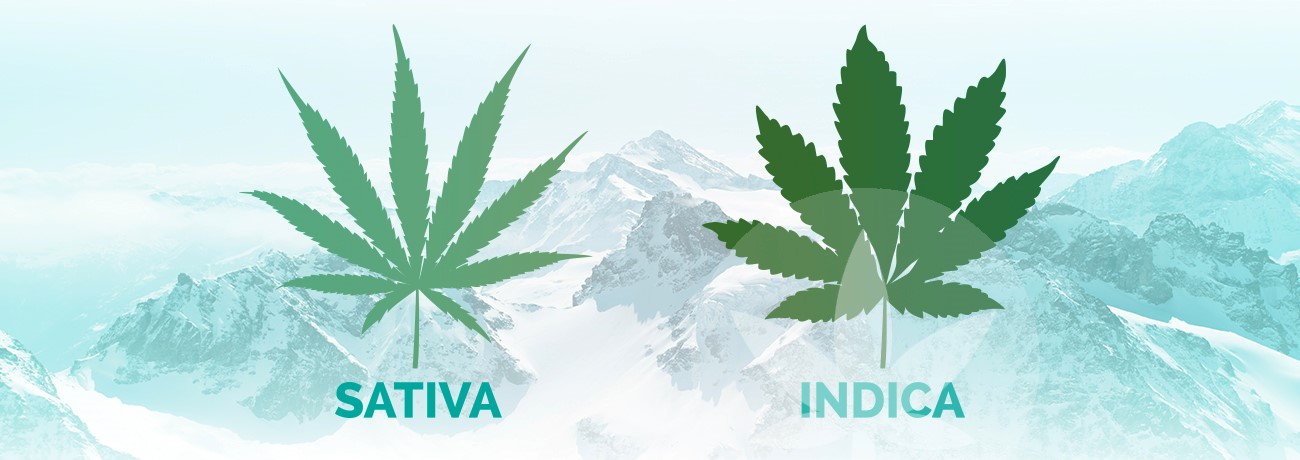
Difference Between Sativa And Indica
Last updated:
Published:
The difference between Sativa and Indica strains has been a topic of great interest for cannabis enthusiasts and researchers alike. These two primary types of cannabis plants, Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica, offer unique effects on the body, making them suitable for various purposes. In this blog post, we will examine the distinctive features of Sativa and Indica strains that lead to their unique effects.
Contents:
- What is Sativa?
- Definition of Sativa
- Characteristics of Sativa Plants
- Benefits of Sativa Strains
- What is Indica?
- Differences Between Sativa and Indica Plants
- Growing Conditions for Sativa and Indica Plants
- Common Uses for Sativa and Indica Strains
- Popular Cultivars of Each Type of Plant
- Popular Cultivars of Each Type of Plant
- How to Choose the Right Strain For You?
- FAQs in Relation to Difference Between Sativa and Indica
- Conclusion
- The entourage effect
From their physical appearance to their chemical composition, we will explore how these differences contribute to the distinct experiences provided by each type of plant. Additionally, we will discuss ideal growing conditions for both Sativa and Indica plants as well as common uses associated with each strain.
Finally, we'll introduce popular cultivars within each category and provide guidance on choosing the right strain based on individual needs and preferences. By understanding the difference between Sativa and Indica strains in-depth, you can make informed decisions when selecting your preferred cannabis products.
The original classification of cannabis Indica was made in 1785 by French biologist Jean-Baptiste Lamarck.

What is Sativa?
Sativa cannabis plants are known to provide an invigorating and stimulating experience, making them a favored choice among those looking for a more mental high. In this section, we'll investigate the meaning, features and advantages of Sativa varieties.
Definition of Sativa
Sativa refers to one of the two primary types of cannabis plants (the other being Indica). These plants have been cultivated for centuries for various purposes such as fiber production, food, medicine, and recreational use. The term "Sativa" comes from Latin and means "cultivated," highlighting its long history in human agriculture.
Characteristics of Sativa Plants
Sativa plants exhibit several distinct features that set them apart from their Indica counterparts:
- Taller growth: Sativas typically grow taller than Indicas with some reaching heights up to 20 feet when grown outdoors.
- Narrower leaves: The leaves on a Sativa plant are generally narrower compared to those on an Indica plant.
- Lanky structure: Due to their height and narrow leaves, these plants often appear lankier than bushy Indicas.
- Fruity aroma: Many users report that the scent profile associated with most sativas is fruity or sweet-smelling rather than earthy or skunky like many indica strains.
Benefits of Sativa Strains
The unique chemical composition found in sativas can provide numerous benefits when consumed either recreationally or medicinally. Some potential advantages include:
- Increased energy: Sativa strains are known for their ability to boost energy levels and provide a more invigorating experience compared to Indicas.
- Creativity enhancement: Many users report that sativas can help spark creativity, making them an excellent choice for artists or those in need of inspiration.
- Mood elevation: The uplifting effects associated with sativas can be helpful in combating symptoms of depression and anxiety.
In the following sections, we will delve into the world of Indica plants and explore how they differ from Sativa strains. Stay tuned.
Sativa, a variety of cannabis, offers distinct features and advantages that make it an attractive selection for many consumers. On the other hand, Indica is another strain of cannabis with its own distinct qualities and advantages.

What is Indica?
In this section, we will explore the world of Indica strains, diving into their unique characteristics and benefits. As a major category of cannabis plants, understanding Indicas can help you make informed decisions about which strain may be best suited for your needs.
Definition of Indica
Indica refers to one of the two primary types of cannabis plants, with its origins tracing back to Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent. These plants are known for their shorter stature, broader leaves, and denser buds compared to Sativa varieties. The effects produced by consuming Indicas tend to be more relaxing and sedative in nature.
Characteristics of Indica Plants
- Growth: Compared to Sativas, Indicas grow shorter (usually between 2-4 feet) with wider leaves that are darker green in color.
- Buds: The flowers or buds on an indica plant are typically dense and compact due to their tighter internodal spacing.
- Maturity Time: Generally speaking, indica strains have a faster flowering time than sativas - often maturing within just eight weeks from germination.
- Cannabinoid Profile: The chemical composition varies among different cultivars; however, indicas usually have higher levels of cannabinoids like CBD relative to THC content when compared with sativa strains.
Benefits of Indica Strains
The soothing properties associated with indicas offer numerous potential benefits for users. Some of the most common advantages include:
- Relaxation: Indicas are known for their calming effects, making them an ideal choice for unwinding after a long day or promoting restful sleep.
- Pain Relief: The higher CBD content in indica strains can help alleviate pain and inflammation, providing relief to those suffering from chronic conditions like arthritis or fibromyalgia.
- Anxiety Reduction: Due to their relaxing nature, indicas may be effective at reducing anxiety levels and helping users feel more at ease.
- Muscle Relaxation: The sedative qualities of these plants have been found useful in easing muscle tension and spasms - particularly beneficial for individuals with multiple sclerosis or other neuromuscular disorders.
In summary, indica strains offer a range of benefits that cater to those seeking relaxation and relief from various ailments. Being aware of the characteristics and potential applications of indica cannabis can help you decide which variety is most suitable for your requirements.
Indica is a cannabis variety that exhibits distinct features and advantages. It is essential to be aware of the contrasts between Sativa and Indica plants when selecting which strain may work best for you.

Differences Between Sativa and Indica Plants
By familiarizing yourself with the differences between Sativa and Indica plants, you can make an informed decision on which strain is best for your needs.
Physical Differences Between the Two Types of Cannabis Plants
Sativa and Indica plants have distinct physical characteristics that set them apart from one another. Here are some key differences:
- Sativa plants tend to be taller with narrow leaves, often reaching heights of up to 20 feet. They also have a lighter green color compared to their counterparts.
- Indica plants, on the other hand, are shorter and bushier with broader leaves. They typically grow no taller than six feet in height and exhibit a darker green hue.
Chemical Differences Between the Two Types of Cannabis Plants
The primary difference between Sativa and Indica strains lies in their unique chemical compositions, specifically regarding cannabinoids such as THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol). These compounds interact with our bodies' endocannabinoid system to produce various effects:
- Sativa strains generally contain higher levels of THC relative to CBD content, resulting in more stimulating cerebral effects like increased focus or creativity.
- Indica strains, conversely, possess higher concentrations of CBD compared to THC levels, which contribute towards relaxation-inducing properties suitable for alleviating stress or promoting sleep.
Effects on the Body When Consuming Different Strains
The contrasting chemical compositions of Sativa and Indica strains lead to distinct effects on the body when consumed:
- Sativa strains are known for their uplifting, energizing, and cerebral effects. They can help increase focus, creativity, and motivation while also providing a sense of euphoria. These characteristics make them ideal for daytime use or social situations.
- Indica strains, in contrast, produce more sedative-like properties that promote relaxation and stress relief. This makes them suitable for evening use or as an aid in managing pain or insomnia.
To learn more about the specific differences between these two types of cannabis plants, check out this comprehensive guide from Medical News Today.
Sativa and Indica plants are two distinct varieties of cannabis, each with its own unique characteristics. By understanding the various characteristics of Sativa and Indica plants, you can determine which one is most suitable for your requirements. Let's explore the optimal environment for cultivating these two varieties of cannabis.
Growing Conditions for Sativa and Indica Plants
Understanding the ideal growing conditions for both Sativa and Indica plants is essential to maximize yield and quality. Each type of cannabis plant has specific requirements in terms of climate, lighting, nutrients, and more. In this section, we will explore the optimal conditions for each strain.
Ideal Growing Conditions for Sativa Plants
Sativa strains thrive in warm climates with plenty of sunlight exposure. Sativa strains originate from regions close to the equator, like Central America, Southeast Asia and Africa; areas that are known for long days of strong sunshine. When cultivating Sativas indoors or outdoors, consider these factors:
- Temperature: Maintain a temperature range between 70-85°F (21-29°C) during daytime hours.
- Humidity: Keep relative humidity levels around 40-50% during flowering stages.
- Nutrients: Provide high levels of nitrogen during vegetative growth followed by phosphorus-rich fertilizers during flowering stages.
- Lights: For indoor grows using artificial lights like LEDs or HPS lamps ensure at least an 18-hour light cycle per day while maintaining adequate distance from plant canopy to prevent overheating issues.
Ideal Growing Conditions for Indica Plants
In contrast to their taller counterparts, Indica strains originate from colder mountainous regions like Afghanistan and Nepal which means they require slightly different environmental parameters than Sativas do when grown under controlled environments such as greenhouses and grow rooms alike.
- Temperature: Maintain a temperature range between 65-80°F (18-26°C) during daytime hours.
- Humidity: Keep relative humidity levels around 30-40% during flowering stages to prevent mold growth and other issues related to excess moisture.
In addition, Indica plants typically have shorter vegetative periods than Sativas which means they will need less time under intense light before transitioning into their flowering phase. This can be achieved by adjusting the light cycle from an 18-hour day length down towards a more standard 12/12 schedule where equal amounts of darkness and illumination are provided throughout each twenty-four hour period.
Overall, understanding the specific growing conditions for both Sativa and Indica strains is crucial in order to maximize yield and quality. By tailoring your cultivation practices according to these guidelines, you'll be well on your way towards producing top-notch cannabis products whether it's for personal use or commercial purposes alike.
Sativa and Indica plants require different growing conditions in order to thrive. It is imperative for cultivators to comprehend the contrasts between these two kinds of cannabis strains when picking which strain they need to develop. Having examined the differences between Sativa and Indica plants, let us now consider how each strain is commonly used.
Common Uses for Sativa and Indica Strains
Both Sativa and Indica strains have unique properties that make them suitable for various purposes, ranging from medical applications to recreational use. In this section, we will explore the common uses of each type of strain.
Common Uses for Sativa Strains
- Energizing Effects: Due to their uplifting and cerebral effects, Sativa strains are often used during daytime activities or social gatherings as they can help boost energy levels and creativity. For example, artists may find inspiration in using a Sativa-dominant strain.
- Mood Enhancement: Many users report that consuming Sativas can lead to an improvement in mood due to their stimulating nature. Sativas are frequently chosen by those with mood issues such as anxiety or depression, due to their capacity for boosting spirits.
- Fatigue Relief: The energizing effects of these strains also make them useful for combating fatigue caused by conditions such as chronic pain or sleep disorders like insomnia.
- Pain Management: While not as potent in terms of pain relief compared to Indicas, some people still find relief with certain types of mild pain when using a Sativa strain.
Common Uses for Indica Strains
- Sleep Aid: The sedative properties found in many Indica strains make them ideal choices for individuals struggling with insomnia or other sleep-related issues. Consuming an Indica before bedtime may promote relaxation and restful sleep throughout the night.
- Pain Relief: In general, Indicas are known for their ability to provide relief from various types of pain, including chronic and acute. This makes them a popular choice among patients suffering from conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, or cancer-related pain.
- Muscle Relaxation: Indica strains have been found to help relax muscles and reduce muscle spasms in some users. For those with conditions like multiple sclerosis or muscular dystrophy, Indica strains may be especially helpful in providing muscle relaxation and reducing spasms.
- Anxiety Relief: Indicas tend to produce calming effects that may help alleviate anxiety symptoms in some individuals. However, it is important to note that not all Indica strains will work the same way for everyone, so experimentation may be necessary to find the right strain.
In addition to these common uses, both Sativa and Indica strains can also be used recreationally by people who enjoy their respective effects on mood and energy levels. It's essential always to consume cannabis responsibly and within legal limits set by your local jurisdiction.
Sativa and Indica strains are commonly used for a variety of purposes, from providing relaxation to energizing effects. Next, let's examine a few famous varieties of both kinds of cannabis.
Popular Cultivars of Each Type of Plant
With the growing interest in cannabis for both recreational and medicinal purposes, many cultivars have been developed to cater to various needs and preferences. In this section, we will explore some popular Sativa and Indica strains that are widely recognized for their unique characteristics.
Popular Cultivars of Sativa Strains
- Sour Diesel: Known for its pungent diesel-like aroma, Sour Diesel is a fast-acting strain that delivers energizing effects perfect for daytime use. Its uplifting properties make it ideal for combating stress, depression, and fatigue. Learn more about Sour Diesel here.
- Haze: This classic Sativa strain has a long history dating back to the 1960s when it was first bred in California by crossing landrace strains from Colombia, Mexico, Thailand, and India. Haze is known for its cerebral high accompanied by an increase in creativity and focus - making it suitable for artistic endeavors or brainstorming sessions. Discover more about Haze here.
- Pineapple Express: A popular hybrid with predominantly Sativa effects derived from its parent strains Trainwreck and Hawaiian; Pineapple Express offers a balanced mix of energy boost coupled with relaxation without causing sedation or drowsiness - perfect as an all-day companion. Find out more about Pineapple Express here.
Popular Cultivars of Indica Strains
- Granddaddy Purple: Often referred to as GDP, this strain is a famous Indica-dominant hybrid that originated in California. This Indica-dominant hybrid is renowned for its soothing effects, helping to reduce pain, tension and sleeplessness - making it a great option when the sun goes down.
- Northern Lights: This legendary pure Indica strain has been around since the early '80s and boasts a strong lineage from Afghani landrace strains. Northern Lights provides full-body relaxation coupled with dreamy euphoria - perfect for unwinding after a long day or combating sleep disorders like insomnia.
- Blueberry: As the name suggests, Blueberry is an Indica-dominant strain with a sweet blueberry aroma and flavor profile. Its calming effects are ideal for those seeking relief from anxiety, chronic pain, or simply looking to relax without feeling overly sedated.
Selecting the right cultivar can significantly impact your overall experience with cannabis; therefore, understanding their unique properties will help you make informed decisions based on your needs and preferences.
Popular Cultivars of Each Type of Plant
In the world of cannabis, there are countless strains available to consumers, each with their own unique characteristics and effects. Here we will discuss some popular cultivars for both Sativa and Indica plants.
Popular Cultivars of Sativa Strains
Sativa strains are known for their uplifting and energizing effects, making them ideal choices for daytime use or social situations. Some well-known Sativa cultivars include:
- Sour Diesel: A classic strain with a pungent aroma and long-lasting cerebral high that is perfect for combating stress and depression.
- Haze: This legendary strain boasts a creative buzz coupled with an invigorating body high, making it great for artistic endeavors or outdoor activities.
- Jamaican Dream: With its sweet tropical flavors and quick-acting euphoric effects, this strain is perfect for those looking to start their day on a positive note.
- Pineapple Express: Known as much for its delicious fruity taste as its balanced head-highs, Pineapple Express offers users increased focus while still providing relaxation.
Popular Cultivars of Indica Strains
Indica strains are often sought after for their relaxing and sedative effects, making them ideal choices for nighttime use or to alleviate stress. Some well-known Indica cultivars include:
- Northern Lights: This iconic strain is known for its powerful body high that can help with pain relief, insomnia, and anxiety.
- Granddaddy Purple: With its distinct grape aroma and potent relaxation effects, this strain is perfect for those seeking a peaceful night's sleep or relief.
- Afghan Kush:An ancient landrace strain hailing from the Hindu Kush mountain range, Afghan Kush offers users deep relaxation coupled with strong medicinal properties to combat ailments such as nausea and pain.
- G-13:This mysterious strain boasts an interesting backstory involving government experiments but is best known today for its intense relaxation capabilities that make it ideal for treating stress-related conditions.
The wide variety of cannabis strains available ensures there's something suitable for everyone's needs and preferences. With so many options, it's important to research and experiment with different cultivars to find the perfect match for your individual requirements.
Understanding the distinctions between sativa and indica strains is essential for choosing a strain that best suits your needs. With this knowledge in hand, you can now look into factors such as effects on your body and mind, aroma/taste profiles, THC content levels and more when selecting the right cultivar for you.
How to Choose the Right Strain For You?
Choosing the right cannabis strain can be a daunting task, especially with so many options available in today's market. It is imperative to take into account elements such as desired effects, cultivation environment, and individual inclinations when picking a strain that meets your requirements. To ensure you make an informed decision, this section will provide guidance on key aspects to consider when selecting a strain.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Strain
- Purpose: Determine whether you are looking for medicinal benefits or recreational use. Some strains may be more suitable for specific medical conditions like chronic pain or anxiety relief while others might provide uplifting effects ideal for socializing.
- Effects: Each type of plant has its unique set of effects on the body and mind. Sativa strains tend to produce energizing and creative experiences whereas Indica strains often induce relaxation and sedation (source). Researching individual cultivars can give further insight into their specific properties.
- Tolerance: If you're new to using cannabis or have low tolerance levels, opt for milder strains with lower THC content (source). Gradually increase potency over time as needed.
- Growing Conditions: If cultivating plants at home, take note of each strain's preferred environment (e.g., temperature range) and growth characteristics (e.g., height). This information will help ensure optimal results during cultivation.
Understanding Your Own Needs and Preferences
Ultimately, the best strain for you will depend on your unique needs and preferences. It is vital to try out diverse strains and cultivars to discover what suits you best. Some people may prefer a balanced hybrid that combines the characteristics of both Sativa and Indica plants, while others might lean towards one type over another based on their desired effects.
To further refine your search, consider seeking advice from experienced users or professionals in the cannabis industry such as budtenders at dispensaries (source). They can provide valuable insight into specific strains' properties and help guide you towards an ideal choice based on your personal requirements.
In addition to selecting a suitable strain, it's crucial to consume responsibly by starting with low doses and gradually increasing as needed. Always be mindful of how each strain affects you individually - remember that everyone's experience with cannabis is unique.
FAQs in Relation to Difference Between Sativa and Indica
Is There Really Any Difference Between Indica and Sativa?
Yes, there are significant differences between indica and sativa strains. These differences include their physical appearance, chemical composition, effects on the body, and ideal growing conditions. However, many modern cannabis strains are hybrids that combine traits from both types.
Is Sativa More Psychoactive Than Indica?
Sativa strains tend to have higher THC levels compared to CBD levels, making them generally more psychoactive than indica strains. Indica varieties usually have a higher CBD-to-THC ratio, which results in a more relaxing effect rather than an energetic high associated with sativas.
Are Indica and Sativa Classifications Outdated?
The terms "indica" and "sativa" can be considered somewhat outdated due to extensive crossbreeding of cannabis plants over time. While these classifications still hold some relevance for understanding general characteristics of different strains, it's important to focus on individual strain profiles including cannabinoid ratios (THC:CBD) and terpenes when selecting a suitable variety.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between Sativa and Indica plants is essential for those looking to consume cannabis. Sativa strains tend to provide an energizing effect, while Indica strains are more relaxing. The physical and chemical differences between the two types of plants can affect their growth conditions, common uses, and popular cultivars.
If you're just beginning to use cannabis or are seeking a particular outcome, it's essential to think about your own desires and inclinations when selecting a strain. With so many options available, finding the right one may take some experimentation.
The entourage effect
This is a relatively new theory that believes that the strain levels of a terpenoid called Myrcene is actually more responsible for creating the differences in psychoactive differences between Indica and Sativa than the percentages and concentrations of THC and CBD.
Terpenoids (or terpenes as they are also known) are synthesized in the secretory cells of the plant and production is increased by exposure to light. Terpenes are also mostly found in high concentrations of unfertilized female cannabis plants as they are growing. They are found in many other plants – usually present to protect the plant from pests – and as a result also emit strong scents and flavours. Some people believe that terpenoid research may be the next big “cutting edge” of research in how medical marijuana, in particular, impacts certain kinds of health conditions.
Myrcene itself has specific medicinal properties, including lowering the resistance across the blood-brain barrier, allowing itself and other chemicals to cross the barrier more quickly. It is also not just found in marijuana – in fact it is most widely consumed as part of the essential oils found in citrus fruit. Some people in fact claim that eating certain kinds of citrus, including mango, 45 minutes before consuming marijuana, will result in a faster result and greater intensity.
The term “entourage effect” was coined by Dr. Ethan Russo when he published a paper in the British Journal of Pharmacology describing the synergies of other compounds found in cannabis as well as the fact that they are typically not present in “CBD-only” products. Russo has also suggested that cannabinoid-terpenoid interactions could also produce synergies in the treatment of many chronic conditions – ranging from depression to cancer and bacterial infections.
Terpenes are present in both Indica and Sativa strains of cannabis.
That said, Indica strains tend to have a dominance of myrcene combined with other terpinoids called limonene or a-pinene. Sativa strains, in contrast appear to have more complex terpene profiles.